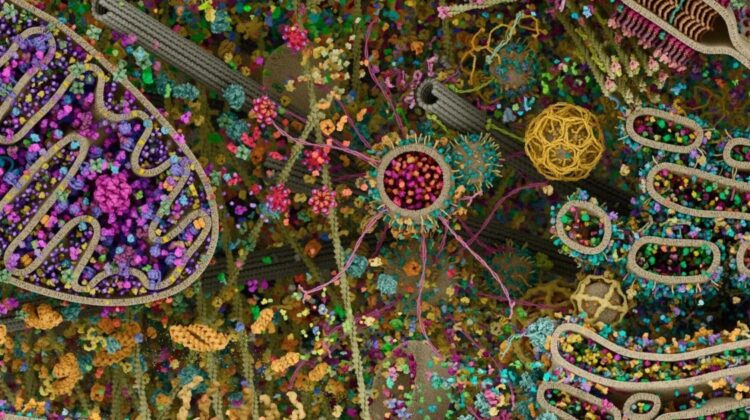
At first glance, it looks like abstract art — a riot of color, spirals, tunnels, and clustered shapes suspended in organized chaos. But this is not a painting. It is one of the most detailed visualizations of a human cell ever produced, revealing the breathtaking complexity hidden inside every living cell of your body.
This remarkable cellular landscape, often referred to as the “Cellular Landscape: Cross-Section Through a Eukaryotic Cell,” was created by Evan Ingersoll and Gael McGill. Their work merges cutting-edge biological research with advanced 3D scientific modeling to construct an ultra-detailed representation of a eukaryotic human cell — the type of cell that makes up your organs, tissues, and systems.
Rather than relying on a single imaging method, the visualization integrates data from multiple high-resolution scientific technologies. X-ray crystallography reveals atomic structures of proteins. Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) helps determine molecular configurations in solution. Cryo-electron microscopy captures frozen molecular machinery in near-native states. These datasets are then combined into a cohesive three-dimensional model, allowing scientists — and the public — to witness the “molecular choreography” happening inside a living cell.
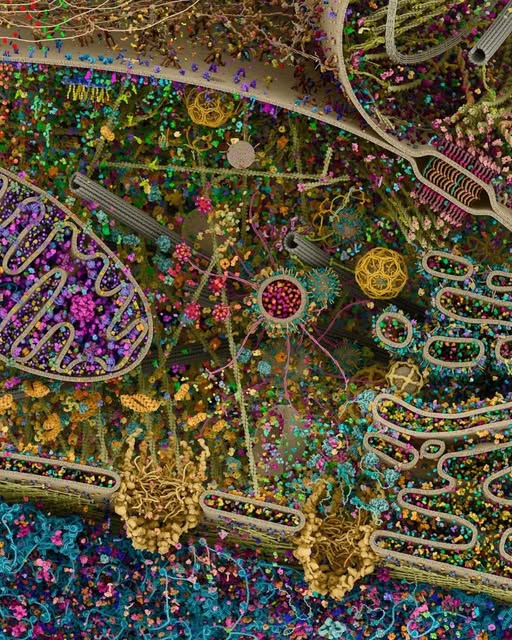
What appears chaotic is, in fact, extraordinarily organized. The large purple, folded structure represents the mitochondrion — the cell’s energy producer. Networks of membranes weave through the cytoplasm. Ribosomes dot the surface of the endoplasmic reticulum, manufacturing proteins. Cytoskeletal filaments stretch like structural highways, guiding transport vesicles that shuttle cargo with precision. Every color, every structure, reflects known biological data scaled to accurate proportions.
More recently, researchers at University of California San Diego and Stanford University developed an advanced cellular map of the U2OS human cell line. Using artificial intelligence, protein localization mapping, and high-throughput microscopy, they created one of the most comprehensive atlases of protein function inside a single human cell. AI-assisted analysis allows scientists to understand not just structure, but dynamic interactions — how proteins move, bind, activate, and regulate life at the microscopic level.
Why does this matter?
Because inside every human body are trillions of cells operating with staggering precision. Diseases such as cancer, neurodegenerative disorders, and metabolic conditions often begin with disruptions at this microscopic scale. The more detailed our cellular maps become, the better researchers can design targeted therapies, precision medicines, and biotechnology innovations.
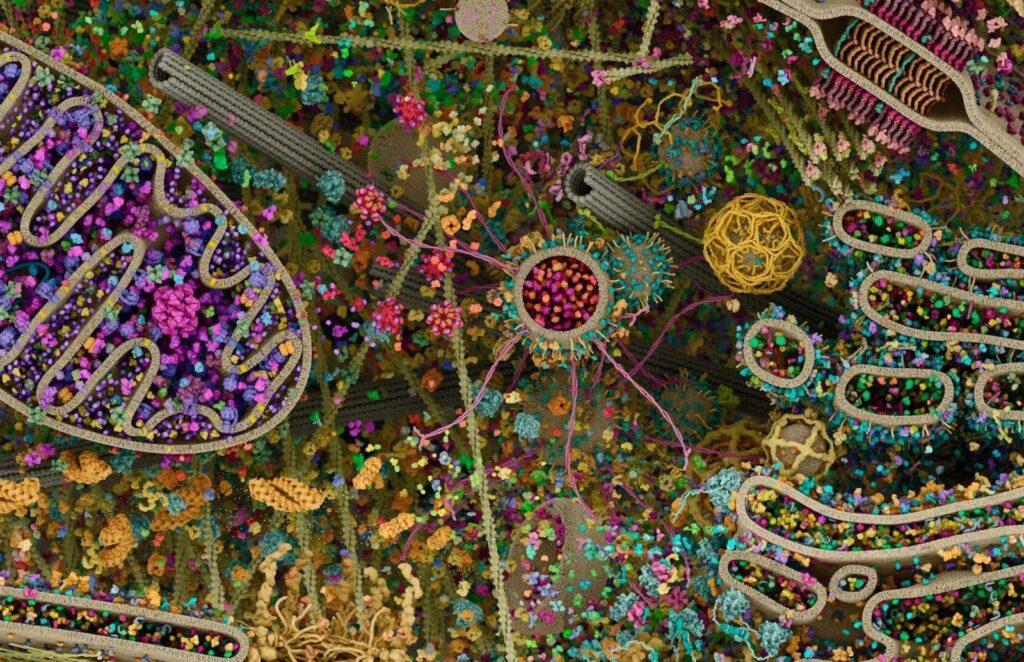

This image is more than scientific art. It represents the convergence of molecular biology, computational modeling, biomedical imaging, and artificial intelligence. It reminds us that beneath our skin lies a universe of organized complexity — a self-regulating system of nanoscopic machines working continuously to sustain life.
The closer we look, the more extraordinary we discover.
High-resolution cellular mapping plays a critical role in modern biotechnology, pharmaceutical development, and precision medicine research. Advanced imaging systems, cryo-electron microscopy platforms, AI-driven protein analysis tools, and molecular modeling software are central to next-generation drug discovery and biomedical innovation. Investment in cellular imaging technology and computational biology infrastructure continues to accelerate breakthroughs in cancer therapy, gene editing, and regenerative medicine.

Leave a Reply